Mucogingival Surgery
Gum Grafting to Cover Exposed Roots
Dr. Evgeny Weinberg
DMD, MSc, PhD, Specialist in Periodontology

What Is Receding Gums?
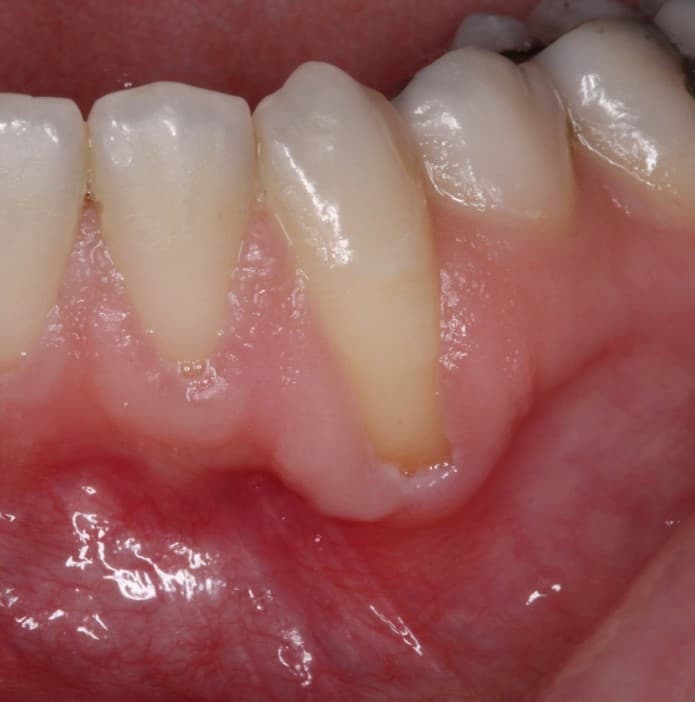
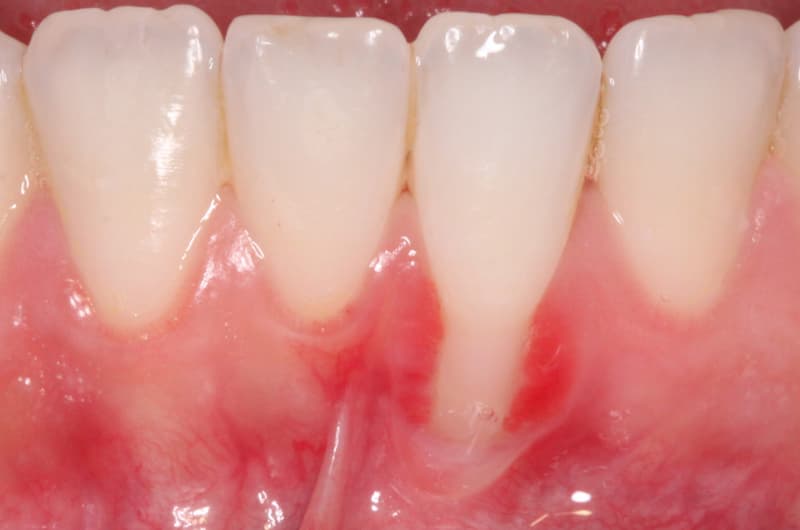
Receding gums, or gum recession, is a slow and gradual process of exposing the root of the tooth to the oral cavity, and many times, especially in the first stages of the phenomenon, it is not noticed.
The first signs include increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods and sometimes the appearance of cervical caries.
When gum recession is caused by gum disease, damage to the tooth’s attachment mechanism will occur.
In addition, this is a very significant aesthetic defect, especially when it comes to the area revealed by a smile.
One of the most effective treatments for the problem is gum transplant surgery.
What Are The Causes Of Receding Gums?
- Inadequate oral hygiene – untreated gum infections and diseases can cause gum recession at different stages of the disease and are one of the signs of gum disease.
- Aggressive brushing – brushing with a hard brush and with strong force may cause trauma to the gums.
- Permanent mechanical stimulation of the gums – piercing in the oral cavity, which causes continuous friction with the gums, or alternatively a crown / restoration (filling), which improperly reaches the edge of the gums. Scratching the gums with external means, such as a toothpick, may also damage the gums and cause them to recede.
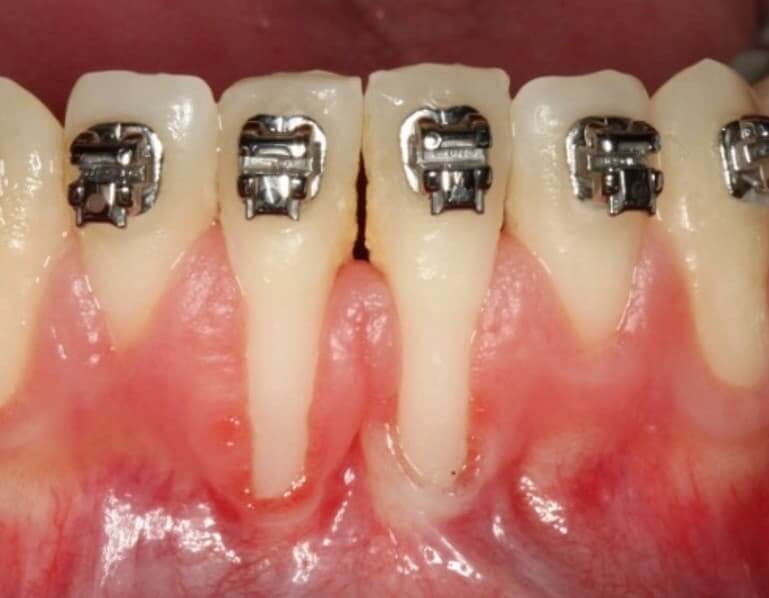
- Teeth alignment – during orthodontic treatment, a tooth shift occurs that can cause a situation where the teeth are pushed out of the bone shell that surrounds them.
- Smoking – more receding gums can be detected in smokers than in non-smokers.
- Genetics – when the patient has delicate and thin gums, there is a greater chance of receding gums, especially in combination with the other factors mentioned above.

What Is Gum Grafting?
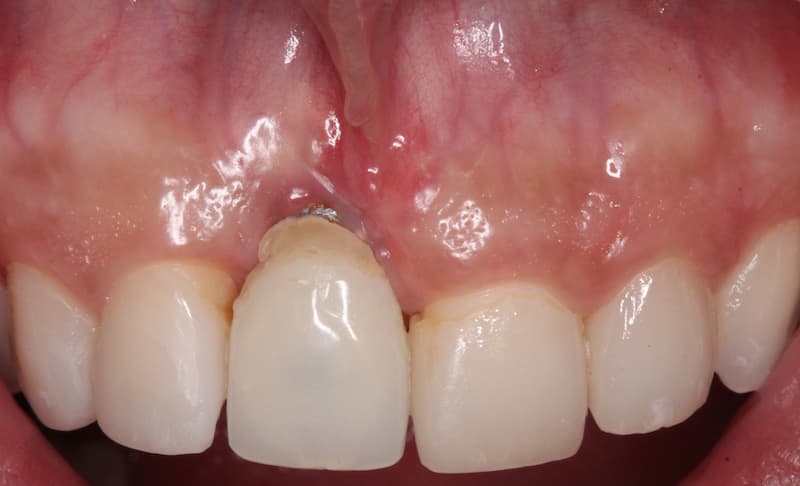
Gum grafting (השתלת חניכיים) is a local surgical procedure in which a sufficient amount of gum tissue is placed, so that it covers the tooth that suffers from receding gums.
The implanted gum tissue is usually harvested from the patient’s hard palate area, or stretched from an area adjacent to the area of receding gums.
In recent years, new techniques and other materials have been developed that are biological substitutes, which can be used as periodontal tissue materials, thus avoiding taking one’s own tissue and injuring another site in the patient’s mouth.
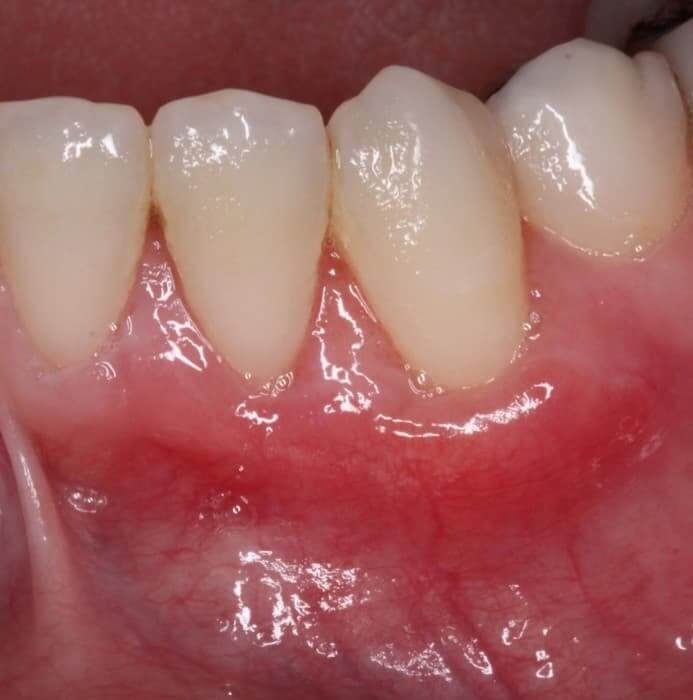
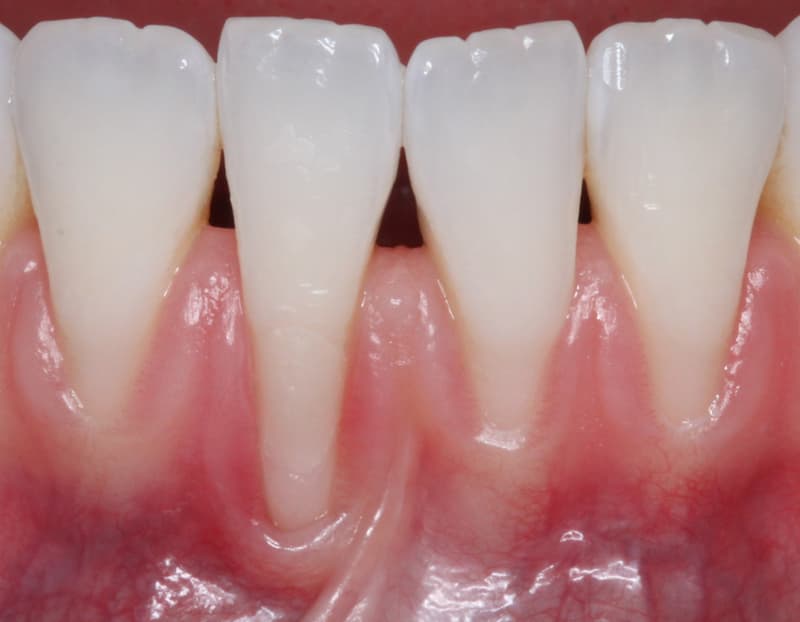
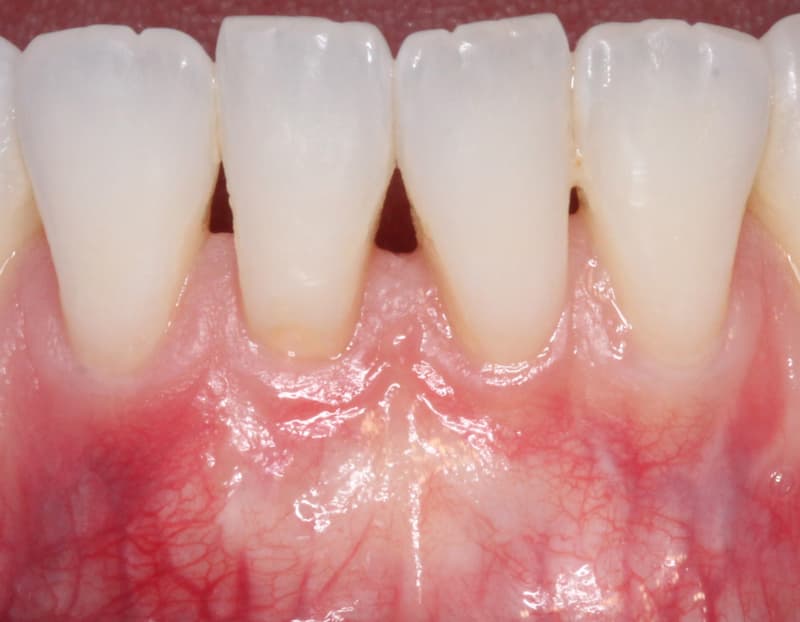
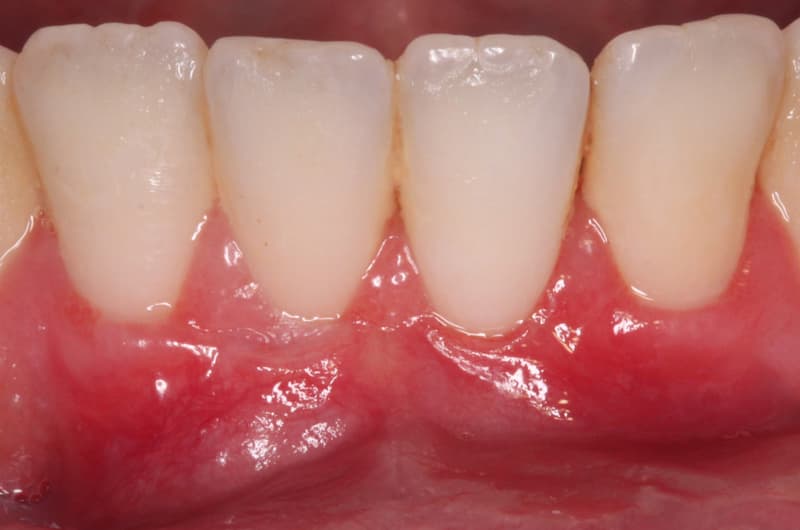
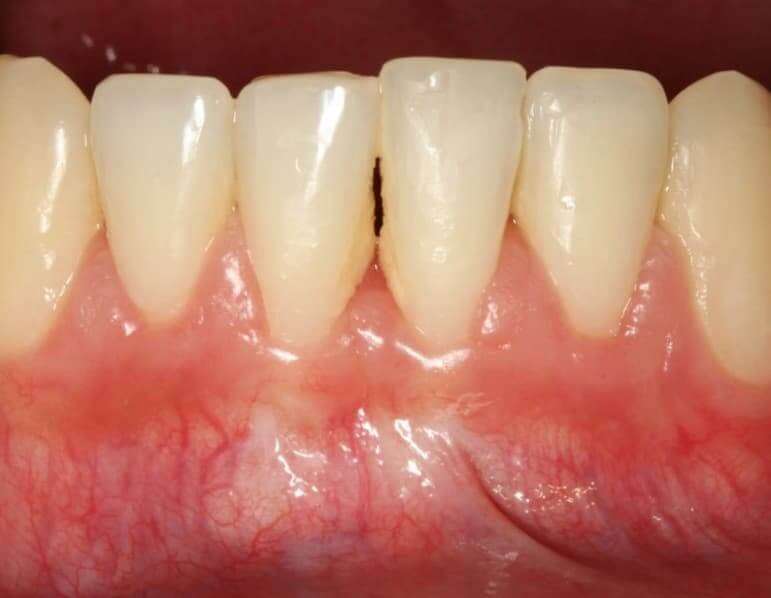
After a period of healing the treated area, the implant becomes an integral part of the gums.
When Should You Perform A Gum Transplant?
- When the patient feels that his aesthetic appearance is damaged as a result of receding gums.
- Sensitivity to cold/heat and temperature changes in the oral cavity which cause damage to the patient’s quality of life.
- When there is serious progress in receding gums over the years, which may be a source of mobility and tooth loss.
What Happens After The Treatment?
During the first two weeks after the treatment, it is recommended to eat soft and cool foods, and it is very important not to brush the area where the transplant was performed and not to floss between the teeth in this area until complete healing.
You can take painkillers according to the periodontist’s instructions and according to the level of pain.
The type of gum graft and its depth affect the intensity of the pain, while if a biological substitute graft was performed and no additional site was injured for tissue removal, the pain is expected to be minor.
Sometimes, the periodontist will give a prescription for antibiotic treatment in order to reduce the risk of infection and inflammation.
General recovery of the mouth is expected to occur about two weeks after the treatment.
About eight weeks after surgery, the transplanted tissues mature and it is possible to determine with certainty what amount of tissue has been absorbed.
In order to optimize the treatment, the periodontist will at this stage evaluate the area where the transplant was performed in order to examine whether a complementary procedure is necessary.
How To Choose A Periodontist?
The surgical treatment for receding gums is a treatment that requires high skill and professionalism.
The beginning of the treatment is the identification of the risk factors for receding gums and their elimination.
If receding gums have occurred, an examination by a specialist in gum diseases (periodontist) is recommended in rder to check whether the case requires and allows treatment.
The degree of success of gum transplant surgery, as well as the risk of complications and the improvement of oral hygiene in the long term, largely depend on the quality, skill and experience of the periodontist you choose.
This is why it is important to have all the information you need to make an informed and well-founded decision.
For information on receding gums contact our dental clinic.
Frequently Asked Questions About Receding Gums
My dentist recommended that I consult a periodontist because of receding that I have. How serious can it be?
Receding gums can appear as a single sign, for example due to aggressive brushing with a hard brush, or as part of gum disease, an infectious disease that also includes damage to the mechanism that holds the teeth (jaw bone).
It is definitely worth consulting with a gum disease specialist (periodontist), as your doctor recommended, in order to diagnose the source of the recession and treat it accordingly.
My gums bleed, especially when I brush my teeth. Is this a natural situation?
Healthy gums should not bleed. Bleeding appears only in the case of gingivitis or even periodontal disease (when the bone that holds the teeth also begins to resorb).
You should contact a periodontist to diagnose the problem.
For the most part, gingivitis is a reversible condition and should be cured to avoid more serious conditions.
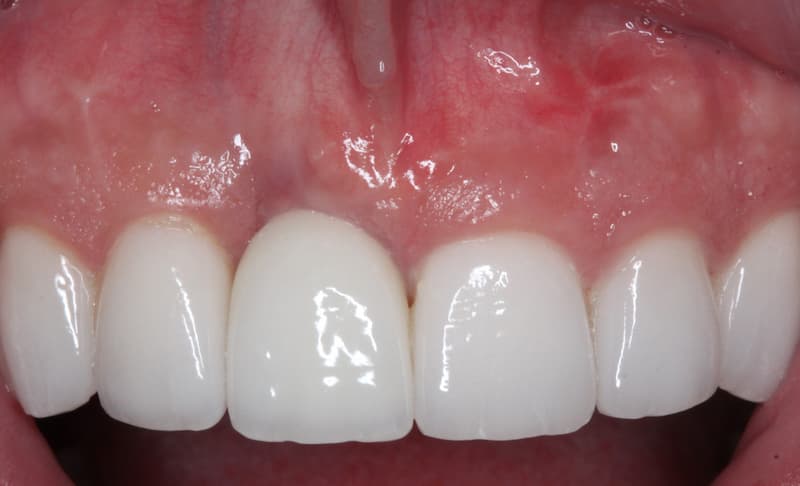
Before and After Mucogingival Surgery
Contact Us
Dr. Evgeny Weinberg DMD, MSc, PhD, periodontist and dental implant.
For further questions about mucogingival surgery, please contact our clinic and we will be happy to help.